Incomplete Dominance
Incomplete Dominance
Incomplete Dominance
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
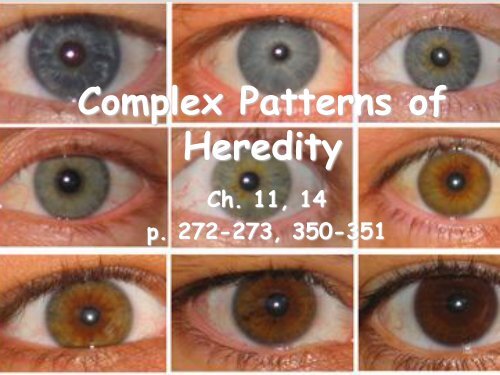
Complex Patterns of<br />
Heredity<br />
Ch. 11, 14<br />
p. 272-273, 350-351
<strong>Incomplete</strong> <strong>Dominance</strong><br />
Codominance<br />
Summary<br />
Traits appear blended<br />
(red + white = pink)<br />
Both traits are<br />
expressed equally<br />
(A + B = AB)
Multiple Alleles<br />
Polygenic Trait<br />
Summary<br />
More than two possible<br />
alleles, but only two<br />
present at a time.<br />
Single trait controlled<br />
by more than one gene.
<strong>Incomplete</strong> <strong>Dominance</strong><br />
• Heterozygous offspring show a phenotype<br />
that is in-between the phenotypes of the<br />
homozygous parents<br />
• Neither allele is dominant<br />
Snapdragon<br />
Flowers<br />
RED + WHITE =<br />
PINK
<strong>Incomplete</strong> <strong>Dominance</strong><br />
W<br />
W<br />
R R<br />
RW RW<br />
RW RW<br />
THE ALLELES REMAIN DISTINCT……ONLY THE<br />
PHENOTYPE APPEARS BLENDED.
Codominance<br />
•2 dominant alleles are expressed<br />
equally at the same time<br />
Ex:<br />
Blood types<br />
“Roan” cattle<br />
Red + White = Red & White<br />
ROAN
Homozygous<br />
Type A blood<br />
Codominance<br />
+<br />
Homozygous<br />
Type B blood<br />
=<br />
Type AB
<strong>Incomplete</strong> <strong>Dominance</strong><br />
Codominance<br />
Summary<br />
Traits appear blended<br />
(red + white = pink)<br />
Both traits are<br />
expressed equally<br />
(A + B = AB)
Multiple Alleles<br />
•Genes with 3 or more alleles<br />
•Only 2 alleles are present at a time<br />
Ex: Blood Types: A, B, AB, O
Blood Types<br />
Phenotype Genotypes<br />
Type A I A I A or I A i<br />
Type B I B I B or I B i<br />
Type AB I A I B<br />
Type O ii
Polygenic Traits<br />
• Traits controlled by two or<br />
more genes that interact<br />
• Ex: eye color, skin color,<br />
hair color, height
Multiple Alleles<br />
Polygenic Trait<br />
Summary<br />
More than two possible<br />
alleles, but only two<br />
present at a time.<br />
Single trait controlled<br />
by more than one gene.
Environmental Effects<br />
(copy this)<br />
• Phenotype is a combination of genetic<br />
and environmental influences<br />
–Example: Himalayan rabbit fur color<br />
depends on body temperature. The<br />
ears, nose, and feet are dark because<br />
they are cooler.
Human Genetics
Difficulties in Studying<br />
• Controlled<br />
experiments are<br />
not possible<br />
• Small numbers of<br />
offspring per<br />
generation<br />
• Long periods<br />
between<br />
generations<br />
Human Heredity
Sex Determination<br />
• Autosomes – body chromosomes – first 22<br />
pair<br />
– Same in both male and female<br />
• Sex Chromosomes – 1 pair, last pair<br />
– XX – Female<br />
– XY - Male
X X<br />
X XX XX<br />
Y<br />
XY XY<br />
XX = 50%<br />
XY = 50%<br />
You always have a 50% chance of having<br />
a girl and a 50% chance of having a boy!
Sex-Linked Traits<br />
• Traits controlled by recessive genes located on<br />
sex chromosomes<br />
• Usually found on the X chromosome<br />
• More common in males<br />
• Ex:<br />
– Hemophilia – missing a blood clotting protein, 1<br />
in 10,000 males<br />
– Color blindness – red/green is the most<br />
common, 1 in 10 U.S. males<br />
– Muscular dystrophy – progressive weakening<br />
and loss of skeletal muscle, 1 in 3000 U.S. males
Sex Linked Traits<br />
• Hemophilia – blood clotting<br />
enzyme<br />
is absent<br />
– Queen Victoria’s family<br />
affected
Sex Linked Traits<br />
• Red – Green Colorblindness – individuals<br />
cannot distinguish between these two colors
Sex Linked Traits<br />
• Duchene<br />
Muscular<br />
Dystrophy –<br />
wasting away of<br />
skeletal muscle
X R<br />
Y<br />
X r<br />
Y<br />
X R<br />
X R X R<br />
X R Y<br />
X R<br />
X R X r<br />
X R Y<br />
X r<br />
X R X r<br />
X r Y<br />
X r<br />
X r X r<br />
X r Y<br />
Females<br />
•X R X R = normal<br />
•X R X r = carrier<br />
•X r X r = disease<br />
Males<br />
•X R Y = normal<br />
•X r Y = disease
Sex – Limited Traits<br />
• Controlled by genes located in the<br />
autosomes<br />
• Only expressed in the presence of sex<br />
hormone<br />
• Only expressed in one gender<br />
• First seen at puberty (hormones<br />
produced in large enough quantities
• Examples:<br />
Sex – Limited Traits<br />
– Male bird’s<br />
colorful plumage<br />
– Beard growth in<br />
males<br />
– Milk production<br />
in females
Sex Influenced Traits<br />
• Traits that are caused by a gene whose<br />
expression differs in males and females<br />
• Also located on autosomes<br />
• Expressed in the presence of male or female<br />
hormones<br />
• Example: male pattern baldness<br />
– BB = normal<br />
– Bb = males bald, females normal<br />
– bb = males and females bald
Hereditary Disorders<br />
• Techniques for detecting genetic disorders<br />
– Amniocentesis – technique used that<br />
removes and studies amniotic fluid<br />
during pregnancy;<br />
– identifies only<br />
chromosomal disorders
Hereditary Disorders<br />
• Karyotyping – an<br />
enlarged photo of<br />
the chromosome<br />
pairs (map) to<br />
identify any<br />
abnormalities in the<br />
chromosomes
Pedigree Charts<br />
• Shows how a trait and the genes that control it<br />
are inherited within a family<br />
• Identifies the presence or absence of particular<br />
trait in members of each generation
Pedigree Charts<br />
• Males = Square<br />
• Females = Round<br />
• Generations = Roman Numerals (I, II, III, IV)<br />
• Individuals = Numbered or Named<br />
• Trait Expressed = Filled in<br />
• Normal = Empty<br />
• Carrier = Half filled