The World Is Full of Holocaust Deniers
A new survey suggests that many Asians, Africans, Middle Easterners, young people, Muslims, and Hindus believe that facts about the genocide have been distorted.
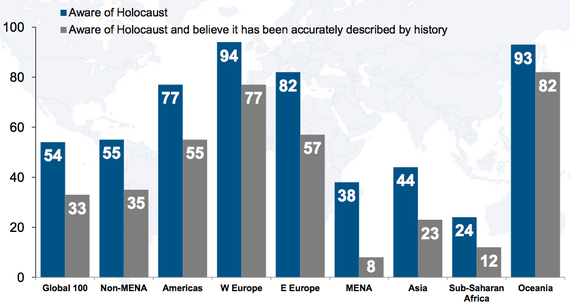
Only 54 percent of the world's population has heard of the Holocaust.
54 percent.
This is the most staggering statistic in a new survey by the Anti-Defamation League (ADL) of more than 53,000 people in over 100 countries, conducted by First International Resources. But that figure speaks to only those who have heard of it: Only a third of the world's population believe the genocide has been accurately described in historical accounts. Some said they thought the number of people who died has been exaggerated; others said they believe it's a myth. Thirty percent of respondents said it's probably true that "Jews still talk too much about what happened to them in the Holocaust."
Seventy years after the liberation of Auschwitz, two-thirds of the world's population don't know the Holocaust happened—or they deny it.
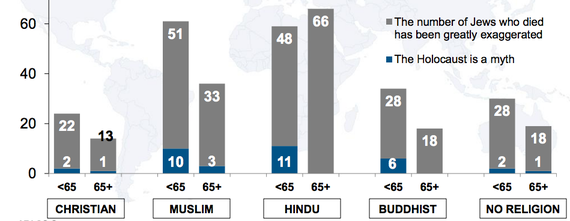
These beliefs follow some unexpected patterns, too. The Middle East and North Africa had the largest percentage of doubters, with only 8 percent of respondents reporting that they had heard of the genocide and believed descriptions of it were accurate. But only 12 percent of respondents in sub-Saharan Africa said the same, and only 23 percent in Asia. People in these groups were likely to say they believed the number of deaths has been exaggerated—just over half of Middle Easterners and a third of Asians and Africans think the body count has been distorted over time.
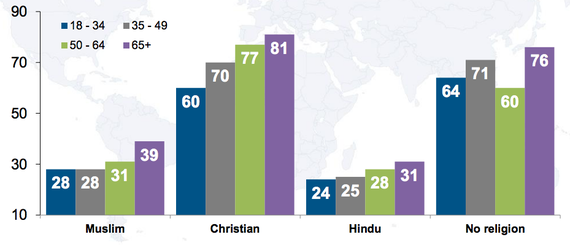
When the data is sliced by religious groups, the results are even more surprising: Hindus were most likely to believe that the number of Holocaust deaths has been exaggerated. Muslims followed closely, and those two groups were distantly trailed by Christians, Buddhists, and those with no religion. In no coincidence, Hindus and Muslims were also significantly less likely to have heard of the Holocaust.
In almost every religious group, people younger than 65 were much more likely to say they believe that facts about the Holocaust have been distorted, and they were less likely to know what the Holocaust is.
The report by the ADL, a Jewish NGO that campaigns against anti-Semitism and discrimination, also covers the prevalence of other anti-Semitic attitudes, including beliefs about Jews' allegiance to Israel, influence in media and business, and likeability. Although the prevalence of Holocaust ignorance and denial was just one small aspect of the survey, it illuminates a powerful fact: As the memory of the genocide grows fainter, attitudes toward Jews—and Israel—are changing. The fate of the Jewish people in the twentieth century was largely centered around the Holocaust: the anti-Semitism that facilitated it, the loss it wrought, and the reflection it prompted. As that history becomes more distant, it's unclear what will animate the Jewish community—and attitudes toward it—moving forward.
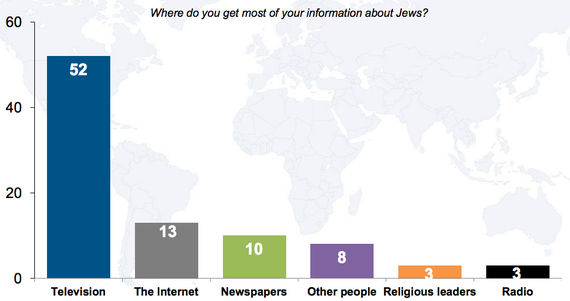
Depressingly, the study does hint at the way most people get their information about Jews and the Holocaust today: