Species Information
Skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) belongs to the mackerel family, Scombridae. Within this species, several variations and subspecies have adapted to specific ocean regions. For instance, the Western Pacific skipjack, Eastern Pacific skipjack, and Atlantic skipjack exhibit subtle differences in size, coloration, and behavior. These variations allow skipjack tuna to thrive in diverse environments across the world’s oceans. Researchers and scientists continuously study these variations to better understand their ecological roles and potential genetic adaptations to local conditions.
Habitat and Range
Skipjack tuna’s habitat and range are influenced by various oceanographic factors, making their distribution complex. They prefer warm waters with temperatures between 18°C and 31°C (64°F – 88°F). Their distribution is influenced by the movement of ocean currents, temperature gradients, and upwelling zones. Understanding these factors is critical for managing skipjack tuna populations and predicting their movements, which can aid fisheries in sustainable harvesting.
Physical Characteristics
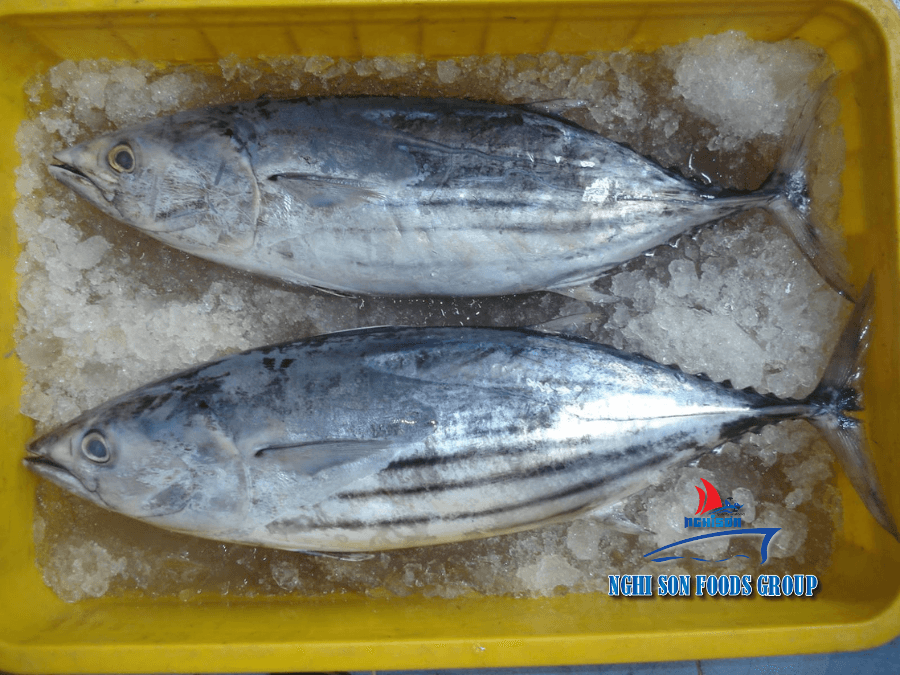
The physical characteristics of skipjack tuna are fascinating. Their streamlined bodies, characterized by a pointed snout, a lateral keel, and a forked tail fin, are perfectly designed for fast, energy-efficient swimming. One of the species’ most distinctive features is the arrangement of seven to nine finlets following the dorsal and ventral fins. These finlets reduce water resistance and enhance their hydrodynamic efficiency, allowing them to swim at high speeds. Additionally, skipjack tuna have remarkable coloration, with a metallic blue-black dorsal side and silver-white undersides, aiding in camouflage and predator evasion.
Catching and Fishing Methods
Sustainable fishing practices are crucial for preserving skipjack tuna populations and reducing environmental impact:
- Pole-and-Line Fishing: This method is highly selective and eco-friendly. It involves catching skipjack tuna individually using baited hooks on fishing lines. The selective nature of this technique minimizes bycatch and is favored by fisheries that prioritize sustainability.
- FAD Management: Fish Aggregating Devices (FADs) are used in some fisheries to attract skipjack tuna schools. However, advancements in FAD technology, such as biodegradable FADs and FAD tracking, aim to mitigate their environmental impact and reduce bycatch. FAD management practices are crucial for maintaining sustainable skipjack tuna harvesting.
Diet and Feeding Habits
Skipjack tuna are opportunistic predators with a diverse diet, which can include:
- Small Fish: They prey on various small fish species, contributing to the regulation of these populations within marine ecosystems.
- Squid: Skipjack tuna also feed on squid, which is an abundant prey item in many parts of their range.
- Crustaceans: Crustaceans such as shrimp are another component of their diet, showcasing their adaptability in response to local prey availability.
Their feeding behavior is influenced by the distribution and abundance of prey species in their habitat. Understanding their dietary preferences and trophic interactions is essential for assessing their role in marine food webs.
Economic Importance
The economic significance of skipjack tuna extends beyond the seafood industry:
- Supply Chain Analysis: Skipjack tuna supports a complex supply chain, from harvesting by fishing vessels to processing in coastal regions near fishing grounds. This supply chain provides employment and income for thousands of people worldwide, making it a cornerstone of many coastal communities.
- Market Dynamics: The global trade in skipjack tuna and tuna products contributes significantly to the economies of both exporting and importing countries. The industry is subject to various market dynamics, including seasonal fluctuations, global demand for seafood, and currency exchange rates, all of which influence skipjack tuna prices and trade.
Understanding the broader economic context and market trends is essential for stakeholders, including fisheries, processors, and consumers, to make informed decisions regarding skipjack tuna.
Regulations and Sustainability
Ensuring the sustainability of skipjack tuna fishing is a global priority:
- RFMO Collaboration: Regional Fisheries Management Organizations (RFMOs) collaborate to establish conservation and management measures for skipjack tuna. These measures include catch limits, monitoring programs, and guidelines to protect the species and its habitat.
- Traceability and Transparency: Emerging technologies, such as blockchain, are being adopted to enhance traceability and transparency in the skipjack tuna supply chain. This allows consumers and importers to verify the legality and sustainability of products, promoting responsible sourcing.
Efforts to manage skipjack tuna sustainably involve close cooperation among nations, organizations, and industry stakeholders to balance economic interests with conservation goals.
Processing and Packaging
Processing and packaging are crucial aspects of maintaining skipjack tuna quality during transportation and storage:
- Advanced Processing Techniques: Innovations in processing techniques are essential for preserving the quality of skipjack tuna products. Methods such as vacuum sealing and flash freezing help maintain the fish’s freshness and texture.
- Sustainable Packaging: Importers can explore sustainable packaging options, such as biodegradable packaging materials and eco-friendly labels, to reduce the ecological footprint of their products. Sustainable packaging aligns with responsible sourcing practices and environmental concerns.
Health Benefits and Culinary Uses
Skipjack tuna offers numerous health benefits and is a versatile ingredient:
- Omega-3 Content: Skipjack tuna is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). These essential fatty acids are associated with various health benefits, including improved cardiovascular health and cognitive function.
- Culinary Versatility: Skipjack tuna is used in various cuisines worldwide, from classic tuna sandwiches and salads to gourmet sushi and sashimi dishes. Its mild flavor and firm texture make it a popular choice for a wide range of recipes, catering to diverse culinary preferences.
Exploring different culinary techniques, recipes, and pairing suggestions allows enthusiasts to fully appreciate the culinary versatility of skipjack tuna.
Import Regulations and Documentation
Importing skipjack tuna requires adherence to complex regulations and documentation requirements:
- Customs and Tariffs: Importers must be aware of customs tariffs and duties, which can vary by country and significantly impact the cost of importing skipjack tuna.
- Food Safety Compliance: Compliance with international and national food safety standards is essential to ensure that skipjack tuna products meet strict quality and safety requirements. This includes rigorous inspections and adherence to Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) principles.
Importers must navigate these regulations to ensure the safe and legal importation of skipjack tuna products.
Environmental Impact
Reducing the environmental impact of skipjack tuna fishing is a critical concern:
- FAD-Free Fishing: Importers can explore the adoption of FAD-free fishing practices, which significantly reduce the environmental impact associated with the use of Fish Aggregating Devices. These practices minimize bycatch and promote responsible fishing.
- Ecosystem-Based Management: Understanding ecosystem-based management approaches highlights efforts to preserve the health of marine ecosystems in which skipjack tuna thrive. These approaches consider the broader ecological context, including protecting sensitive marine habitats and minimizing the impact of fishing on non-target species.
Recipes and Cooking Techniques
For culinary enthusiasts and chefs, skipjack tuna offers a world of possibilities:
- Sous Vide Cooking: Sous vide is a precise cooking method that involves vacuum-sealing the tuna and cooking it in a water bath at a controlled temperature. This technique ensures that the fish is cooked to perfection, retaining its moisture and flavor.
- Artisanal Canning: Home canning allows consumers to create their canned skipjack tuna products, tailored to their tastes. This process involves preserving the fish in jars with flavorful oils and seasonings, providing a unique and customized pantry staple.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.